By Raúl Alonso Huerta
Slide 1
In this first slide we can see the title of our presentation, the group members, Maximilian Rallis, and Raul Alonso Huerta, as well as the title of the course.
Slide 2
In the second slide we will start analysing the sustainability problems of our phones currently, and the reasons behind those problems, although this slide is just a title slide for the topic.
Slide 3
In the third slide we will start explaining the problem of sustainability regarding the smartphone’s chip and motherboard. These components are fundamental for the correct functionality of the phones, making very difficult the changes upon them quite difficult due to the complexity of this systems.
These chips are made by silicon, a precious material, that has shown to be quite difficult to extract due to the specific lands from where it is extracted, making difficult the sustainable approach to this extraction.
Moreover, the energy consumption in this extraction and the furthermore processing is also high, making it a sustainability problem up to some level, depending on how the energy produced for this procedure is done, but considering the main producer is China, the energy required is obtained by unsustainable sources (65% of China’s energy production comes from coal)
On the other hand, the alternatives are not very realistic yet, as the heat dissipation that is required for the material is very high, so further technology must be developed in order to change this material and then, solve the sustainability problem It comes by.
Slide 4
In the next slide we start describing the other sustainability problems.
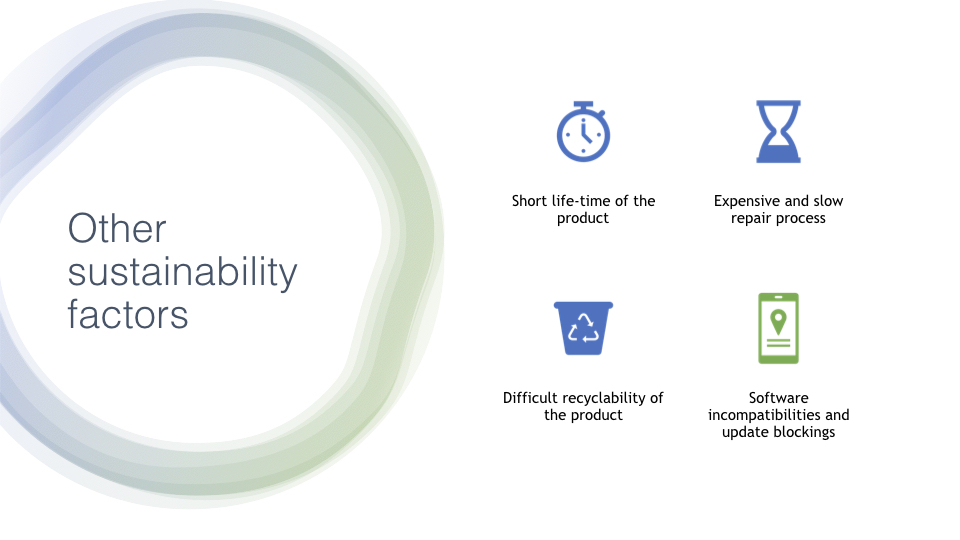
We can start with the short lifetime of phones, a product that usually costs over 400€ but that is used for around 2 years or even less depending on the user, and the model itself. This short time generates a lot of electronic waste, because now everyone needs a phone, so then it is impossible to reduce its use with a realistic point of view.
Continuing with the lifetime, it is aggravated by the fact that the repair process is usually slow and expensive in most of the cases, due to the compression of the components in a small space, that makes that usually when one of the components breaks, it affects the others, making users to decide usually to change the phone rather than repairing it.
Moreover, the phones are difficult to recycle as they have a lot of different materials inside that are not biodegradable, including also very dangerous materials when broken.
Adding up to this, the other problem that appears to them, is that even if the user repairs the phone and takes care of it the functionalities of the phone will soon start to become old and obsolete in many cases due to the lack of updates for old phones, the incompatibility with new applications and some other software problems that might appear that the user cannot avoid. Due to this the user usually changes the phone even though it was working correctly, which is the opposite of circularity.
Slide 5 Slide 6 Slide 7 Slide 8 Slide 9
These parts will be covered in work of my peer Maximilian Rallis
Slide 10
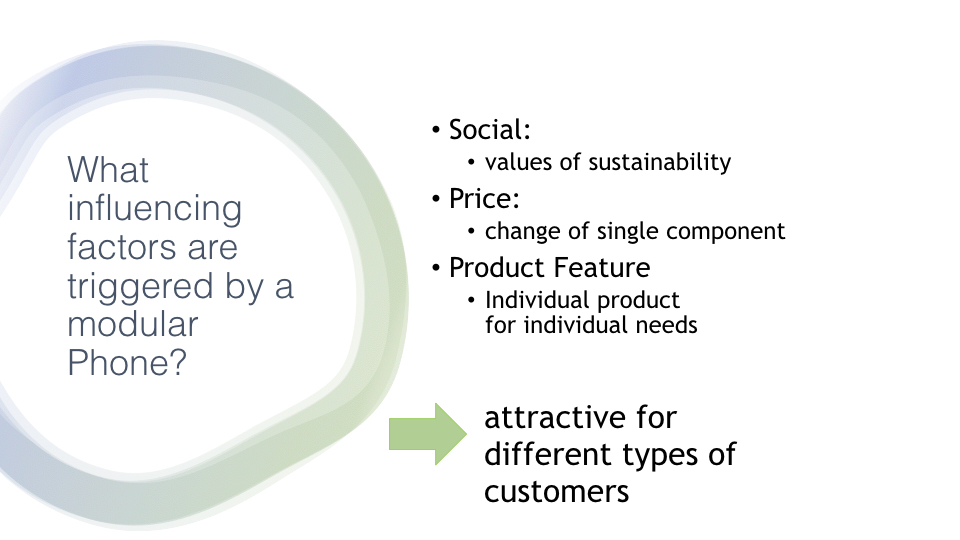
In this slide we present the topic of how our product will influence the market and shift it into a more circular environment (or try it at least)
Slide 11
This slide will show what is the current state of the phone market, and why it is very important to shift to a new market in order to achieve the circularity we are searching for.
First, the market state right now is an oligopoly controlled by a few groups of companies that have a market influence over the 50%. This companies are known by all of us, and they are Apple, Samsung and Xiaomi, in a descending order of importance but with not a high differentiation in terms of market influence. These companies can prevent other companies to enter the market, and then break innovative approaches that usually come by small start-ups that try to change something.
In addition, the market is focused on the necessity of new models every year, due to the necessity of these three companies to surpass the others, so then they short their phone’s lifetime and create incompatibilities among versions in order to hook the user into their products and services to take them for longer time and earn more money. These practices are in the sense of linear economy and generate a lot of sustainability problems at every level of the environment as we have already discussed in the sustainability factors of the smartphone.
In conclusion, the competition of this companies is demolishing start-ups and circular approaches to the smartphone market, at least for the moment, due also to systems like iOS that is controlled by Apple and makes it very difficult to other companies to use this operating system.
Slide 12
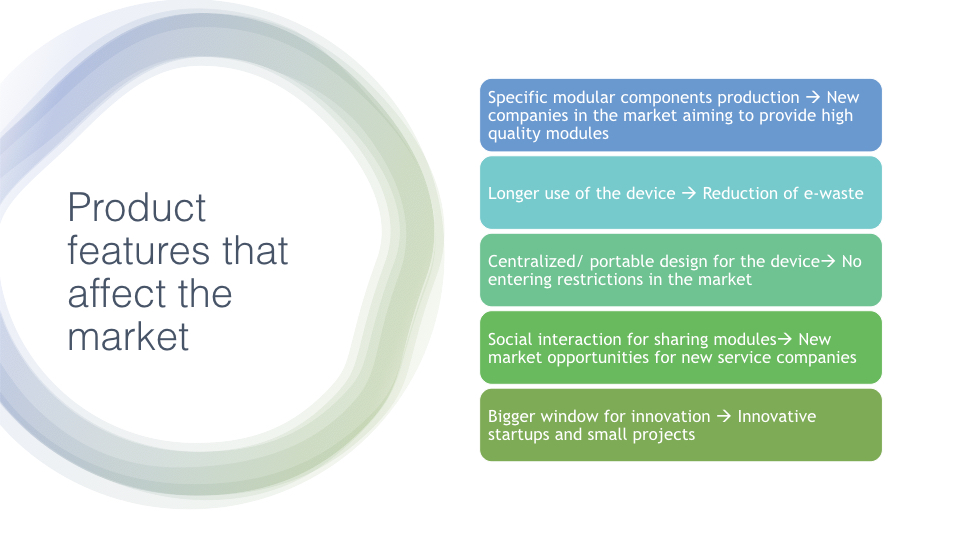
In this slide we will describe the product features that affect the market directly and that might be able to shift it.
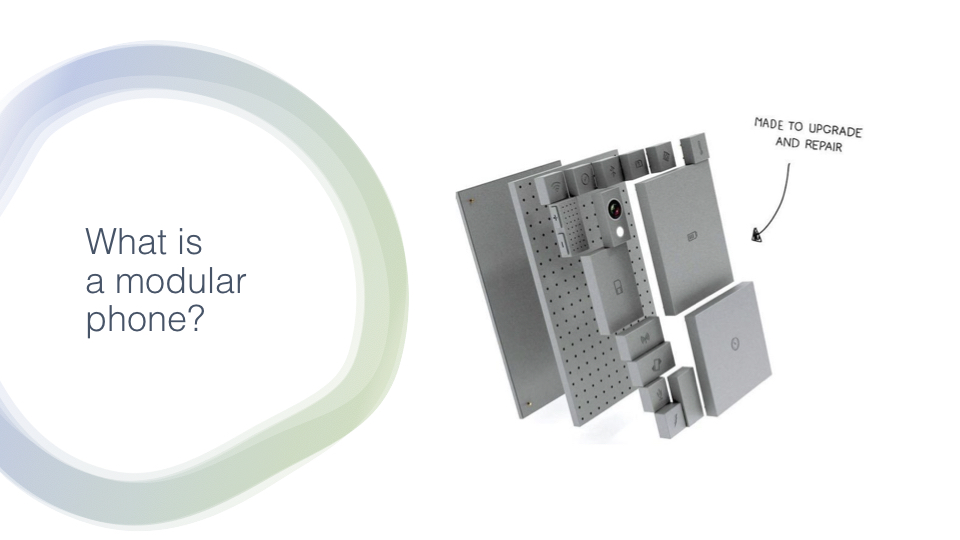
One of the features we need to consider is that the product modularity makes new companies ot be able to enter in this market with the modular components’ productions, that is completely different from the complete phone production that we are used to. In this sense, companies could have different starting points such as photography companies that start making camera modules for the phone as an example, and that could not be affected by the other producers.
The longer use of this device will stop the necessity of releasing new models every year, so then we will have a market more focused on the upgrades of existing models than a market that tries to incentive the user to change current models. This will help to reduce the e-waste generated as we already discussed.
Moreover, the portable and centralized design of the model will prevent old companies to restrict much the entering into the market of new companies. This is very important because this market idea needs to have a lot of different modules in order to work in a good state, adding up with the bigger window for innovation, the small start-ups and circular projects will be able to survive if they do a decent job, making it a much more varied environment.
Finally, I must remark that the interaction for sharing modules opens even more the opportunities the new market is able to offer with the creation of social networks that connects users to test new modules, reusing modules that other users don’t want, or sharing modules among different users to have the opportunity to try modules before buying them, reducing even more the amount of waste that this module generate compared to the complete smartphones previously used.
Slide 13
Finally, the last slide will show how the new market should look like, explaining that the market will become a fragmented environment, which due to the nature of modularity, we will create a diverse ecosystem for the smartphones.
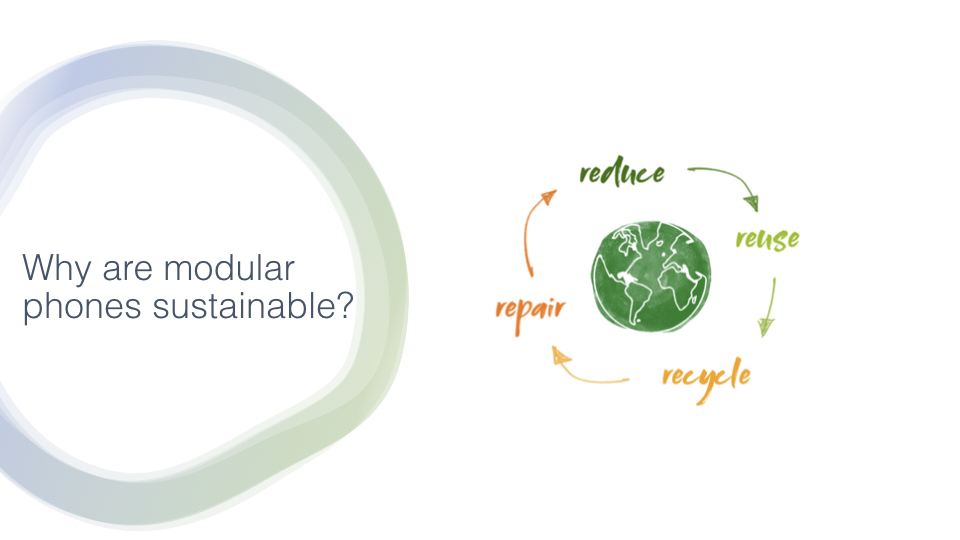
In addition to fragmentation, it is important to remark that circularity will be included into the phone production, re using phone modules, reducing the e waste due to longer lifetime of the devices, repairing modules in an easier way, and recycling the components in a better way, as we can create recycling process for the specific modules, without needing to consider the entire device for that process.